Catalysis of the Thermal Decomposition of Transition Metal Nitrate Hydrates by Poly(vinylidene difluoride)
Lasanthi Sumathirathne, William B. Euler, Polymers, 2021, 13, 3112
Abstract
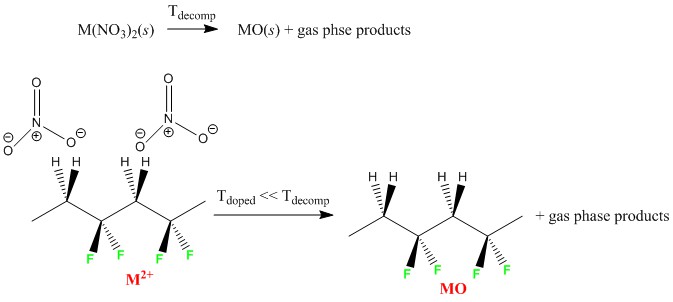
Poly(vinylidene difluoride) (PVDF) doped with transition metal nitrate hydrates are cast into thin films giving a high β‐phase content. Analysis of the thermal behavior of the doped PVDF shows that the decomposition of the metal (II) nitrate hydrates to metal (II) oxides is catalyzed by the PVDF, as evidenced by reduction in the decomposition temperature by as much as 170 °C compared to the pure metal salts. In contrast, there is little to no apparent catalysis for the decomposition of the metal (III) nitrate hydrates. The FTIR spectra of the gas phase decomposition products show H2O and NO2 are the major components for both PVDF‐doped material and the pure metal nitrate hydrates. A mechanism for the role of PVDF is proposed that uses the internal electric field of the ferroelectric phase to orient the nitrate ions and polarize the N‐O bonds.